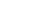
| 标准编号 Standard/Code | 标准名称 Standard Title |
| ASTM G21 | Standard Practice for Determining Resistance of Synthetic Polymeric Materials to Fungi |
4.1 The synthetic polymer portion of these materials is usually fungus-resistant in that it does not serve as a carbon source for the growth of fungi. It is generally the other components, such as plasticizers, cellulosics, lubricants, stabilizers, and colorants, that are responsible for fungus attack on plastic materials. To assess materials other than plastics, use of this test method should be agreed upon by all parties involved. It is important to establish the resistance to microbial attack under conditions favorable for such attack, namely, a temperature of 2 to 38°C (35 to 100°F) and a relative humidity of 60 to 100 %.
4.2 The effects to be expected are as follows:
4.2.1 Surface attack, discoloration, loss of transmission (optical), and
4.2.2 Removal of susceptible plasticizers, modifiers, and lubricants, resulting in increased modulus (stiffness), changes in weight, dimensions, and other physical properties, and deterioration of electrical properties such as insulation resistance, dielectric constant, power factor, and dielectric strength.
4.3 Often the changes in electrical properties are due principally to surface growth and its associated moisture and to pH changes caused by excreted metabolic products. Other effects include preferential growth caused by nonuniform dispersion of plasticizers, lubricants, and other processing additives. Attack on these materials often leaves ionized conducting paths. Pronounced physical changes are observed on products in film form or as coatings, where the ratio of surface to volume is high, and where nutrient materials such as plasticizers and lubricants continue to diffuse to the surface as they are utilized by the organisms.
4.4 Since attack by organisms involves a large element of chance due to local accelerations and inhibitions, the order of reproducibility may be rather low. To ensure that estimates of behavior are not too optimistic, the greatest observed degree of deterioration should be reported.
4.5 Conditioning of the specimens, such as exposure to leaching, weathering, heat treatment, etc., may have significant effects on the resistance to fungi. Determination of these effects is not covered in this practice.
1. Scope
1.1 This practice covers determination of the effect of fungi on the properties of synthetic polymeric materials in the form of molded and fabricated articles, tubes, rods, sheets, and film materials. Changes in optical, mechanical, and electrical properties may be determined by the applicable ASTM methods.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Test Requirement 测试要求:
合成高分子材料抗菌法的测定 Standard practice for determining resistance (须廯毛廯菌)
Sample Size 样品数量 / 送样规格: 5cm x 5cm x 10pcs (thickness less than 1cm)
Lead Time / TAT (Turn Around Time) 测试周期: 常规服务 Regular service 30 working days
Report Summary 报告摘要: